Buy VPS Servers – Virtual Private Servers (VPS) have revolutionized the way businesses and individuals host websites, applications, and manage online projects. Offering a powerful combination of dedicated server resources and affordability, VPS servers provide an ideal solution for those seeking more control and flexibility than traditional shared hosting environments.
This introduction will explore what VPS servers are, their benefits, and why they are a popular choice in the realm of web hosting and server management. Whether you’re a startup looking to scale your online presence or a developer needing a robust testing environment, understanding VPS servers is essential for optimizing your digital operations.
What is Buy VPS Servers?
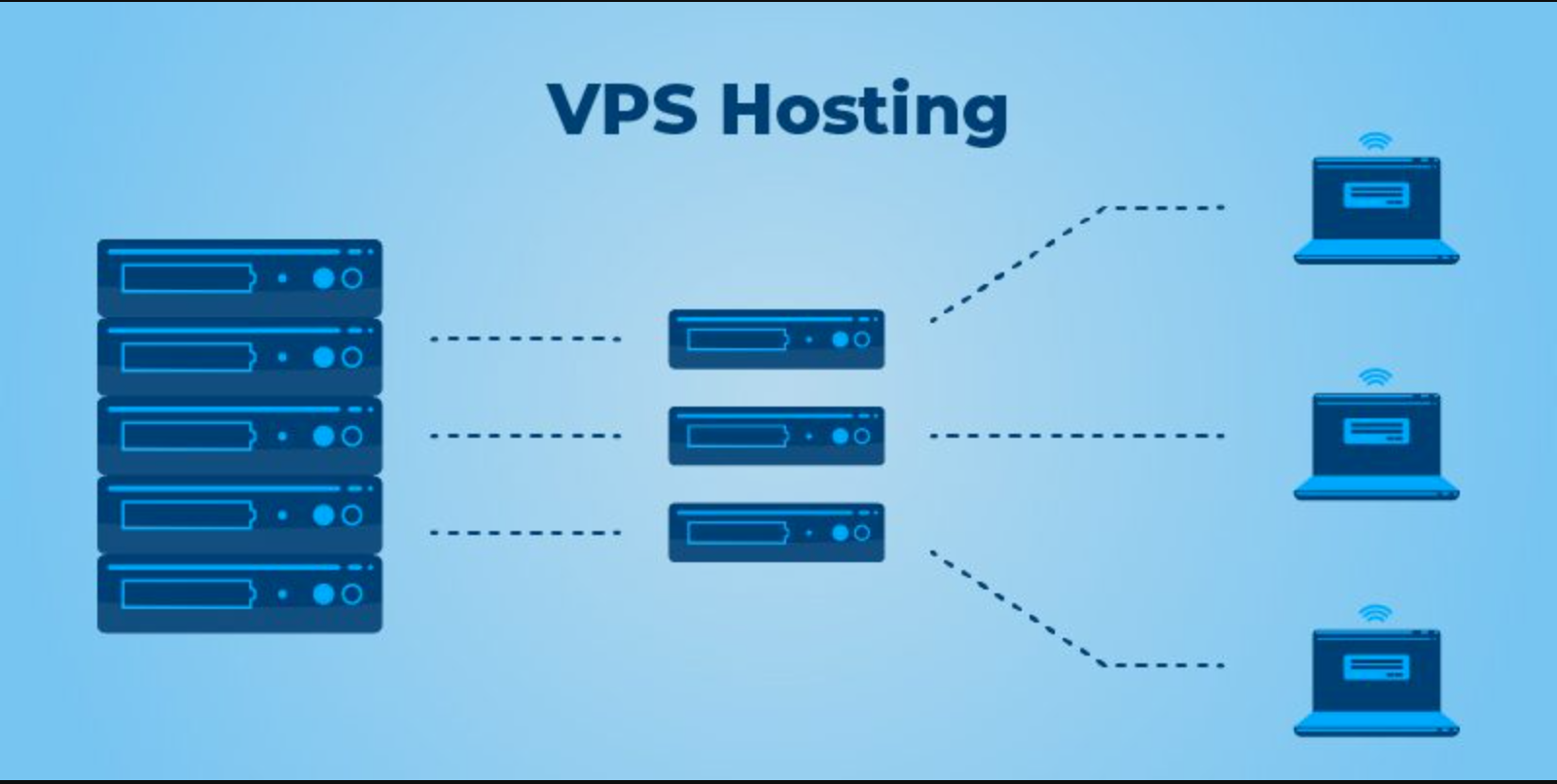
“Buy VPS Servers” refers to the process of purchasing Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting services from a provider. A VPS is a virtualized server environment created within a larger physical server. Unlike shared hosting where multiple websites share resources on a single server, a VPS allocates specific resources like CPU, RAM, and storage to each user, providing a more isolated and customizable hosting environment.
When you buy VPS servers, you typically select a plan based on your resource needs and budget. Providers offer various plans with different levels of CPU cores, RAM sizes, storage capacities, and bandwidth limits. Some VPS hosting services are managed, meaning the provider handles server maintenance tasks like updates, backups, and security patches. On the other hand, unmanaged VPS hosting gives you full control over server management, requiring you to handle all technical aspects.
Buying VPS servers involves choosing a provider that meets your performance requirements, offers reliable uptime guarantees, and provides adequate customer support. It’s essential to consider factors like server location (for latency considerations), scalability options, security features (such as firewalls and DDoS protection), and pricing structures (monthly or annual plans).
What is a VPS Server?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a virtualized server that acts as a dedicated server within a larger physical server. Unlike shared hosting, where resources are distributed among multiple users, a VPS allocates a specific portion of the physical server’s resources to each user. This provides a balance between the affordability of shared hosting and the performance of dedicated hosting.
Difference Between VPS and Shared Hosting
Shared hosting means multiple websites reside on a single server, sharing its resources like CPU, RAM, and storage. This can lead to slower performance if one website consumes more resources. On the other hand, VPS hosting provides isolated resources for each user, ensuring consistent performance and better security.
VPS vs. Dedicated Hosting
While a VPS offers a portion of a physical server’s resources, dedicated hosting gives you an entire server to yourself. Dedicated hosting provides superior performance and control but comes at a higher cost. VPS serves as a middle ground, offering more control and performance than shared hosting at a more affordable price than dedicated hosting.
Why Choose a VPS Server?
Enhanced Performance
VPS servers offer better performance compared to shared hosting because resources are not shared. This means your website or application can handle more traffic and run more smoothly.
Improved Security
With a VPS, your data is isolated from other users. This isolation reduces the risk of security breaches caused by other users on the same server. Additionally, you have the flexibility to implement your own security measures.
Greater Control and Customization
A VPS provides root access, allowing you to customize the server environment to your needs. You can install software, configure settings, and optimize performance without the restrictions typical of shared hosting environments.
Types of VPS Hosting
Managed VPS Hosting
Managed VPS hosting means the hosting provider takes care of server management tasks such as updates, security patches, and backups. This is ideal for users who prefer to focus on their websites or applications rather than server maintenance.
Unmanaged VPS Hosting
Unmanaged VPS hosting provides you with a server and its resources, but you are responsible for all maintenance and management tasks. This option is suitable for users with technical expertise or those who want complete control over their server.
Cloud VPS Hosting
Cloud VPS hosting leverages cloud infrastructure to provide scalable VPS solutions. It allows for easy resource scaling and provides high availability, as your VPS can run on multiple physical servers.
Key Features of VPS Servers
Root Access
Root access gives you administrative control over your VPS, enabling you to install and configure software, manage files, and execute commands.
Scalability
VPS servers are highly scalable, allowing you to adjust resources like CPU, RAM, and storage as your needs grow. This ensures your server can handle increased traffic and workload.
Dedicated Resources
With a VPS, you receive dedicated resources that are not shared with other users. This results in consistent performance and reliability.
Operating System Choices
VPS hosting often provides a range of operating system options, such as Linux distributions (Ubuntu, CentOS) and Windows Server. This flexibility allows you to choose the OS that best fits your requirements.
How to Choose the Right VPS Provider
Evaluating Performance and Uptime
Look for providers that guarantee high uptime (99.9% or higher) and offer robust hardware specifications. Reliable performance ensures your website or application remains accessible and responsive.
Customer Support
24/7 customer support is crucial, especially if you encounter technical issues. Ensure the provider offers multiple support channels, such as live chat, phone, and email.
Pricing and Plans
Compare different providers’ pricing and plans. Consider what resources (CPU, RAM, storage) are included and whether there are any hidden fees. Choose a plan that offers the best value for your budget.
Data Center Locations
The location of data centers can affect your server’s performance. Choose a provider with data centers close to your target audience to reduce latency and improve load times.
Setting Up a VPS Server
Initial Setup Steps
Once you’ve chosen a provider and plan, you’ll need to set up your VPS. This involves creating an account, selecting an operating system, and configuring your server settings.
Installing the Operating System
Most VPS providers offer various OS options. Choose the one that suits your needs and follow the provider’s instructions to install it on your VPS.
Configuring Server Settings
After the OS is installed, you’ll need to configure your server. This includes setting up user accounts, configuring the firewall, and optimizing performance settings.
Securing Your VPS
Security is paramount. Ensure you install security updates, configure firewalls, and set up regular backups to protect your data and server.
Common Uses for VPS Servers
Hosting Websites
VPS is ideal for hosting websites, especially those with high traffic or requiring custom configurations. It offers better performance and reliability than shared hosting.
Running Applications
A VPS can host various applications, from content management systems (CMS) to customer relationship management (CRM) software, providing the necessary resources and control.
Developing and Testing
Developers use VPS for testing and development environments, allowing them to simulate production conditions and ensure their applications run smoothly before deployment.
Game Servers
VPS can host game servers, providing the resources and control needed to run online multiplayer games with minimal lag and high reliability.
Pros and Cons of VPS Servers
Advantages
-
Performance: Dedicated resources ensure consistent performance.
-
Control: Root access allows full customization.
-
Scalability: Easily upgrade resources as needed.
-
Security: Isolated environment enhances security.
Disadvantages
-
Cost: More expensive than shared hosting.
-
Management: Requires technical knowledge if unmanaged.
-
Complexity: Setup and maintenance can be more complex than shared hosting.
Cost Considerations
Pricing Models
VPS pricing varies based on the provider, resources, and management level. Common models include monthly, yearly, or pay-as-you-go.
Comparing Costs with Other Hosting Types
While VPS is costlier than shared hosting, it provides better performance and control. It’s less expensive than dedicated hosting while offering many of the same benefits.
Budgeting for a VPS
Consider your resource needs and budget accordingly. Factor in additional costs like software licenses, backups, and potential management fees.
Performance Optimization Tips
Resource Allocation
Ensure your VPS has enough CPU, RAM, and storage to handle your workload. Monitor usage and upgrade resources as needed.
Monitoring Tools
Use monitoring tools to track server performance, detect issues, and optimize resource usage. Tools like Nagios and Zabbix can help maintain server health.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Keep your server’s software up-to-date with the latest security patches and performance improvements. Regular maintenance can prevent issues and enhance performance.
Security Best Practices
Firewall Configuration
Set up a firewall to block unauthorized access and protect your server from attacks. Configure rules to allow only necessary traffic.
Regular Backups
Regularly back up your data to ensure you can restore your server in case of data loss or corruption. Consider automated backup solutions and store backups securely offsite.
DDoS Protection
Implement DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) protection mechanisms to mitigate the risk of service interruptions due to malicious traffic floods. Many VPS providers offer built-in DDoS protection or partner with specialized providers.
Scaling Your VPS
Vertical Scaling
Increase the resources (CPU, RAM, storage) of your existing VPS plan vertically to handle increased traffic or workload demands. Vertical scaling involves upgrading your current plan without changing providers.
Horizontal Scaling
Expand your VPS horizontally by adding more virtual servers to distribute the load. This approach enhances redundancy and fault tolerance while accommodating growth.
Auto-scaling Solutions
Utilize auto-scaling solutions that automatically adjust resources based on real-time traffic and workload demands. This ensures optimal performance during peak periods without manual intervention.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Connectivity Problems
Troubleshoot connectivity issues such as network configuration errors or firewall settings that may block incoming or outgoing connections.
Resource Limitations
Identify and resolve resource constraints that affect server performance, such as insufficient RAM or CPU throttling under heavy load.
Security Breaches
Respond to security incidents promptly by investigating the cause, patching vulnerabilities, and enhancing security measures to prevent future breaches.
Conclusion
In conclusion, VPS servers offer a versatile hosting solution suitable for a wide range of applications, from hosting websites to running complex applications and game servers. With enhanced performance, greater control, and improved security compared to shared hosting, VPS servers provide flexibility and scalability for growing businesses and developers.
Choosing the right VPS provider involves considering factors like performance guarantees, customer support, pricing, and security features. By understanding your needs and evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision to leverage the benefits of VPS hosting for your online presence or applications.